Welcome to a beginner’s guide on the basic computer terms. The cyber-world sure is confusing these days with a ton of jargon, technical words, and abbreviations. But fear not, let us walk through the essential ones in this guide, explained in simple English. Read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Hardware Hardware |
 Software Software |
 Internet Internet |
 More More |
 The End The End |
HARDWARE
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
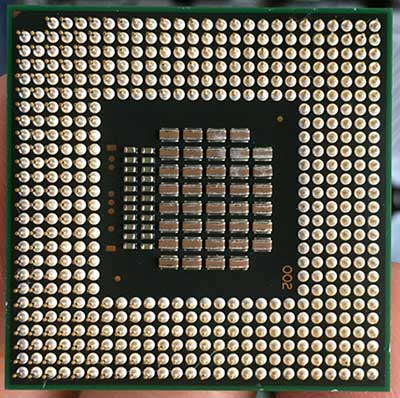
The brain of the computer that does data processing.
RANDOM-ACCESS MEMORY (RAM)

Fast and volatile “short-term memory”, computers usually use RAM as temporary data storage for the more immediate processes. Once the power is switched off, everything inside the RAM will be lost.
READ-ONLY MEMORY (ROM)
Fast and non-volatile “long-term memory” of computers. Unlike RAM, ROM will retain the data even after the power is switched off.
HARD DISK DRIVE (HDD)

Large capacity permanent storage, where we install all the applications and keep our data. These are also commonly known as “mechanical hard disks”, due to the fact that it is driven by a motor and have several read/write heads.
SOLID-STATE DRIVE (SSD)

This is also a hard disk, but it uses a different technology. SSDs are made of “one solid piece of circuit board full of memory chips” instead of spinning data platters like mechanical drives. Thus, they are rightfully called “solid-state” because they have no moving parts.
M.2 NVME SSD
 The later version of “hard disks”, has a much smaller footprint that favors mobile devices.
The later version of “hard disks”, has a much smaller footprint that favors mobile devices.
- SSD – You already know this. Basically “hard disk made up of solid memory chips”.
- M.2 – The form factor. 22mm wide and varies in length.
- NVME – Non-volatile memory express, basically the interface design. NVME SSDs are directly connected to the CPU, allowing faster read/write speeds.
FLASH DRIVE

An external device to store data. This is also known as a pen drive or thumb drive.
BITS & BYTES
How is memory capacity measured in a computer? In the smallest unit, a computer can only understand “1 or 0” – We call this a single bit of data.
- 1 byte = 8 bits.
- 1 kilobyte = 1000 bytes.
- 1 megabyte = 1000 kilobytes.
- 1 gigabyte = 1000 megabytes.
- 1 terabyte = 1000 gigabytes.
- 1 petabyte = 1000 terabytes.
KEYBOARD

Well, the device that we type on to input data to the computer.
- A standard “qwerty” full-sized keyboard has 104 keys.
- Tenkeyless (TKL) keyboards are essentially full-sized keyboards without the number pad. 87 keys.
- Most laptops have a compact 75% (80-84 keys) or 65% (66-69 keys) keyboard.
MOUSE

The device that we use to move the cursor on the screen.
MONITOR

You are reading off one right now.
- CRT – Cathode Ray Tube, the older “bulky monitor”. Pretty much extinct now, and can only be found in museums.
- LCD – Liquid Crystal Display, the “slim monitor” technology that replaced CRT.
- LED – Light-Emitting Diodes, the “common Joe” that we see everywhere now.
PRINTER

A device to print paper documents.
3D PRINTER
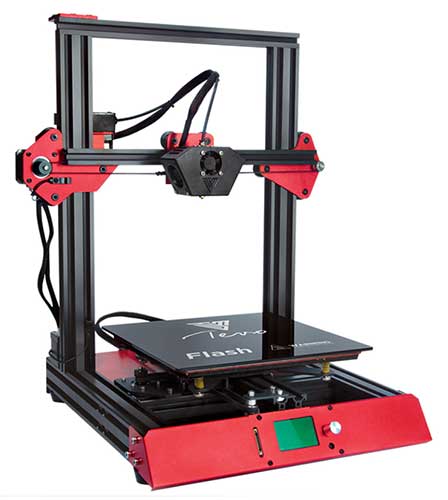

An “advanced” printer that prints objects by melting a spool of thread plastic called “filament”.
UNIVERSAL SERIAL BUS (USB)
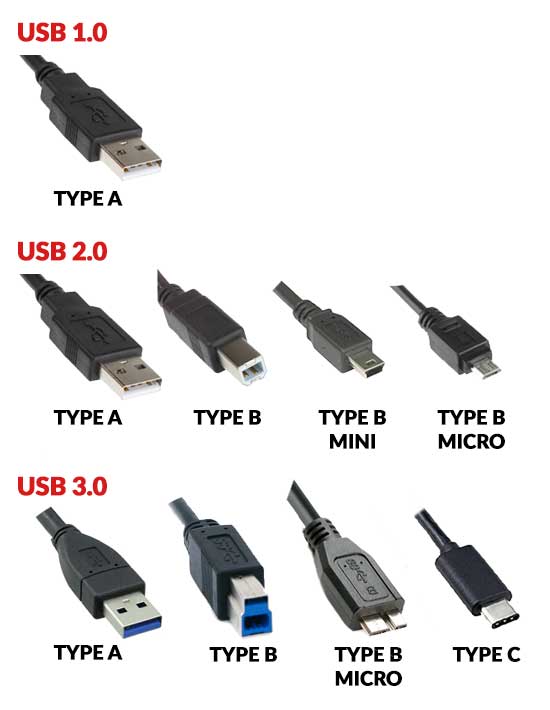

The de facto standard connector that we see on nearly every device.
SOFTWARE
OPERATING SYSTEM (OS)
System software that serves as the platform. Manages the hardware, the system resources, and also allows users to install other applications. The common operating systems are Windows, Mac OSX, Android, iOS, and Linux.
APPLICATION (APP FOR SHORT)
Software that we install on computers to do all kinds of things – Word processing, browsing the Internet, listening to music, watching videos, etc…
FREEWARE, SHAREWARE, ADWARE
- Freeware – Applications that are free.
- Shareware – Applications that can be used for free for an evaluation period. But will require a fee thereafter.
- Adware – Applications that are free, but supported by advertisements.
DRIVER
Software that we install in operating systems, to enable certain hardware to work properly.
FIRMWARE
Something like a driver. But firmware is permanently embedded into devices, not installed in operating systems.
GFX
Abbreviation for “graphics”.
OFFICE SUITE
- Word Processor – Software that we use to create text documents.
- Spreadsheet – Once upon a time, we use a pen, paper, and ruler to draw tables. In computers, we have “spreadsheets”.
- Slides – Presentation slides.
MALWARE & VIRUS
Bad software that is designed to cause damage to computers.
GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACE (GUI)
Pronounced as “gooey”, basically all the windows, buttons, icons, and toolbars that you interact with on a computer.
INTERNET & NETWORKING
INTERNET
A global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP)[b] to communicate between networks and devices.
The Internet (spelled with a capital “I”), is a combination of 2 words “inter” and “network”. Simply put, a global collection of computer networks.
WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW)
An information space where documents and other web resources can be accessed through the Internet using a web browser.
Yes, the “Internet” quite essentially refers to the global infrastructure of computer networks. While WWW refers to the online content, the “information space”.
UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR (URL)
In simple terms, the web address. For example, https://red-dot-geek.com
INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER (ISP)
The company that provides you with the service of accessing the Internet.
1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G
“G” is short for “generation”, and these are referring to the generations of the wireless mobile network. I.E. First generation, second generation, fifth generation, etc… Of course, the later generations are more advanced than their ancestors.
WIFI
Short for “wireless fidelity”. Not to be confused, WiFi and “G” are 2 different technologies. “G” networks literally carpet entire cities, while WiFi spans across homes and offices.
MODEM

Short for modulator-demodulator. The device that connects you to the Internet. They actually come in many shapes and sizes these days, wired ones that use copper wires, fiber optics, and even wireless modems that use the mobile network.
WIRELESS ROUTER
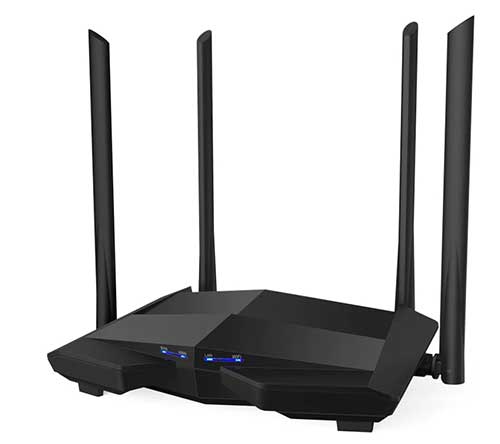

Used to create your own private WiFi network. Connect this to a modem to share the Internet connection among many devices.
FIREWALL

A security device that protects your devices against virus, malware, and the bad guys. Can be in the form of a dedicated network device, or software installed on a computer.
WEB BROWSER
Software that you are using right now to access the information on the WWW.
HYPER TEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE (HTML)
Used to create web pages, the backbone behind them; Specifies how the web pages are structured.
COOKIE
Not the ones we eat… Cookies are “tokens” that are sent from a website to the user. They are used to properly identify the users, and to store small amounts of data – Things such as a shopping cart, or your personal preferences on that website.
CAPTCHA
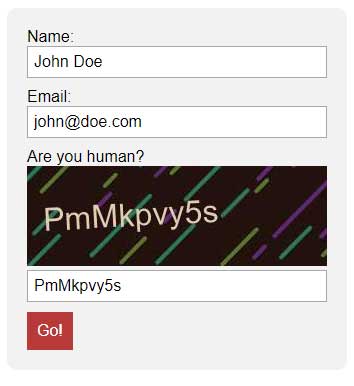
Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. Yep… CAPTCHA for short. A technique used to fight spam, by asking the user to complete a simple game, or to enter a series of characters.
MORE
There are actually a lot more computer terms… So many that we can write an entire encyclopedia with. If you are interested in learning more, here are 2 of the more complete lists:
THE END

Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope that this has helped you to better understand, and if you have anything to share with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy computing. May the cyber force be with you.

Thank you so much. When you are a novice one is afraid to seem unknowledgeable so afraid to ask simple questions about terms.
definitely guiding and enthusing writeup.