Welcome to a guide on the types of computer storage devices and media. Over many years in the digital world, people have invented tons of storage devices and media. Just which is which? Let us walk through the common types of storage devices and media in this guide – Read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Magnetic Storage Magnetic Storage |
 Optical Storage Optical Storage |
 Flash Memory Storage Flash Memory Storage |
 Network Storage Network Storage |
 Paper Storage Paper Storage |
 Useful Bits & Links Useful Bits & Links |
 The End The End |
MAGNETIC STORAGE

Let us now start with one of the most traditional forms of data storage, using magnets. In layman’s terms, the north/south pole of the magnet can be used to represent a data bit. Put a bazillion mini magnets into a small box, and we get a magnetic storage device.
1) HARD DISK DRIVE (HDD)

The regular Joe that we find in most computers. Hard disks store data in magnetic platters and use read-write heads just like the old-school retro record players. Because of the motor and read/write head, these are also commonly known as “mechanical hard disks”.
2) MAGNETIC CARD/STRIPE

Ever notice the black stripe behind credit cards and ATM cards? Ever wonder why people swipe these black stripes across a machine? That is because the black stripe is actually magnetic and contains a unique identification number. Now that you know, keep your card safe and don’t ever damage that stripe.
3) TAPE

In short, tapes are just long magnetic strips. The oldies should know this one very well, and there are various types of tapes – Cassette tapes for audio, videotapes, and even tape drives for server backup. Even though we no longer use cassettes and videotapes these days, tapes for server backup are still in use.
4) FLOPPY DISK

Oldies should know this one as well. Floppy disks are essentially “magnetic paper encased in plastic”, and there are 3 common sizes:
- Floppy disks started with a crazy large 8-inch format.
- It later “shrunk” down to 5 1/4 inches.
- Then finally down to 3 1/2 inches.
But floppy disks are no longer in use today due to their very limited storage space and manufacturing cost.
5) ZIP DISK

Following up sometime in the mid-1990s, floppy disks could no longer keep up with the amount of data. Something called a “zip disk” then replaced it – With a single zip disk being able to hold up to 70 or more floppy disks. It remained popular until CDs took over in the early 2000s.
6) SUPER DISK

The super disk is a competitor to the zip disk, but sadly, it was not too popular and died without making a big splash.
OPTICAL STORAGE

These are what ended the floppy and magnetic disks – Optical discs that use lights and lasers to store data.
7) COMPACT DISC (CD)

I guess you can call these the so-called first generation of mainstream optical discs. CDs used to be manufactured in factories only, but after the invention of writable and rewritable discs (CDR and CDRW), they took over the market by storm.
8) DIGITAL VERSATILE DISC (DVD)

DVDs are pretty much still optical discs, but it holds more data. Call it the “improved version of CDs” if you want, and they hold about 6 .5 times more than a normal CD.
9) BLU-RAY (BR)

Yet another improved version of the optical disc and BR discs hold about 5 times more data than normal DVDs. But one thing to take note of – Most Blu-ray players are backward compatible, but the older devices are not forward compatible; A Blu-ray player is most likely able to read all CDs, DVDs, and BR. But the older CD players will not be able to read BR discs.
FLASH MEMORY STORAGE

Different from the “usual memory”, flash memory actually retains the data even without power. They used to be pretty expensive in the old days and are reserved for very specialized fast data storage. But thanks to technology, they have become very affordable and common these days.
10) FLASH DRIVE

A modern-day staple and you should have seen one of these before. These are also commonly called the “pen drive” or “thumb drive”, depending on where you are in the world.
11) MEMORY CARDS

Another modern-day staple. There are many different types of memory cards, but they are all flash memory at the heart:
- Secure Digital (SD)
- Mini SD
- Micro SD
- XQD
- Compact Flash (CF)
- Memory Stick
- MultiMedia Card (MMC)
12) SOLID STATE DRIVE (SSD)

SSDs are the so-called “later versions” of hard disks. But instead of using magnetic platters, SSD is one solid circuit board full of memory chips. Thus, they are rightfully called “solid-state” because they have zero moving parts.
The “no mechanical parts” design makes SSDs very popular and suitable for mobile laptops and tablets – They save a ton of space, are lightweight, and they are immune to shakes (shock proof).
13) M.2 SSD
 Well, this is still an SSD. It just has a smaller footprint, about the size of a stick of gum.
Well, this is still an SSD. It just has a smaller footprint, about the size of a stick of gum.
NETWORK STORAGE

After the Internet boom sometime in the 2000s, several networks and Internet-based storage solutions rose to fame.
14) NETWORK-ATTACHED STORAGE (NAS)

The NAS is actually nothing more than an enclosure… It’s just a box that has wireless capabilities. Put a hard disk or plug a flash drive into the enclosure, and it becomes automatically shared on the wireless network. All devices connected to the wireless network can then access those storage devices. Pretty cool.
15) CLOUD STORAGE
Cloud storage is not a device, but rather, storing data on the Internet… If you trust the Internet enough. Here are a few good free cloud storage providers:
PAPER STORAGE

What!? Paper can be used to store data as well? Yes, and you have probably already used it before. Paper is actually one of the oldest data storage media, and it is still very much still in use today.
16) BARCODES

There are many different types of barcodes, and you have probably seen these everywhere – In newspapers, posters, publications, and products.
- QR Code
- Codabar
- Code 25, Code 11, Code 32
- EAN
- UPC
Scan one of these, and they will give you a serial number, a promo code, or even a website address. An alternate way to think of barcodes is “alphabets for the machines”.
17) PUNCH CARD
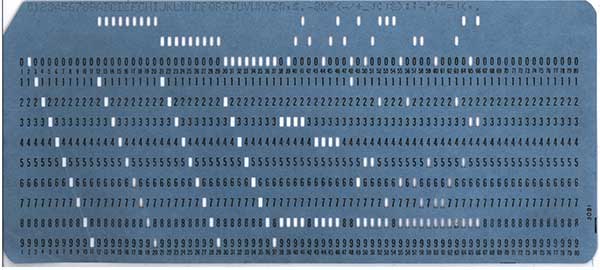
This is an ancient way to record data. This is a piece of paper with printed numbers, time slots, and/or alphabets – Just punch a hole on the appropriate one. These are probably still in use at some factories or restaurants for timekeeping.
18) OPTICAL MARK READING (OMR)
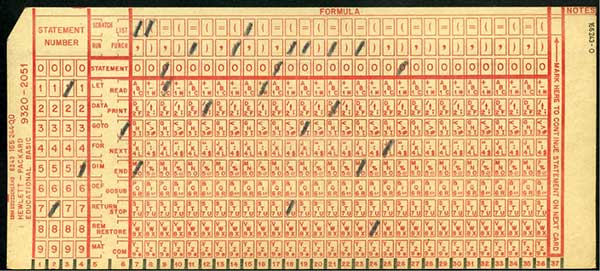
Remember these “shade the circles” papers you get in examinations? The multiple-choice-questions? That is called optical mark reading (OMR), and it works pretty much the same as punch cards. Except that you shade the slot instead of punching a hole.
USEFUL BITS & LINKS

That’s all for this guide, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
INTERNAL VS EXTERNAL STORAGE
- Internal storage – Storage devices that you put inside the computer, such as hard disks.
- External storage – Storage devices and media that you insert into a computer, such as memory cards.
Yep. It’s that straightforward.
PRIMARY, SECONDARY, AND TERTIARY STORAGE
- Primary storage – This usually refers to the fast, volatile memory that is used for processing temporary data variables. Turn off the power, the data is lost.
- Secondary storage – The internal storage for permanent data storage. Turn off the power, the data is still intact.
- Tertiary storage – “Extra” external storage that is used for backup or transferring data.
BITS & BYTES
For you folks who do not already know:
- Computers can only understand 1 and 0 – We call that single 1 or 0 a bit.
- 8 bits form 1 byte.
- 1000 bytes is called 1 kilobyte.
- 1000 kilobytes as 1 megabyte, 1000 megabytes as 1 gigabyte, and 1000 gigabytes as 1 terabyte.
So yep – That is a lot of zeros when it comes to data storage.
LINKS & REFERENCES
- Computer Basics: 10 Examples of Storage Devices – TurboFuture
- Computer Data Storage – Wikipedia
- Storage Device – Computer Hope
THE END

Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope that this has helped you to better understand the world of digital storage, and if you have anything to share with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and may the digital force be with you.

Short notes but good enough for beginners!
Loveeeee this website. Will recommend!