Welcome to a beginner’s guide on basic Internet knowledge. So you have just hopped into the Internet cyber world? Or maybe you just want to learn more? Either way, the Internet has become such a huge part of humanity that it is hard to ignore.
But with many years of history, the Internet is definitely not an easy one to understand – There are a lot of underlying technologies, lingoes, and cultures. Let us walk through some of these basics, read on!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Basics & History Basics & History |
 Technical Basics Technical Basics |
 Common Services Common Services |
 Useful Bits & Links Useful Bits & Links |
 The End The End |
INTERNET BASICS & HISTORY

First, let us start with a short introduction and history of the Internet – What it is, and how it came into existence.
WHAT IS THE INTERNET?
The internet is a globally connected network system that uses TCP/IP to transmit data via various types of media. The internet is a network of global exchanges – including private, public, business, academic and government networks – connected by guided, wireless and fiber-optic technologies.
That sure is a very technical definition of the Internet. But in simple terms, the Internet (spelled with a capital “I”) is made up of 2 words – “Inter” and “Network”. As you can guess, that is basically a ton of computer networks interlinked with each other, on a worldwide scale.
WHAT IS THE WORLD WIDE WEB (WWW)?
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is the world’s dominant software platform. It is an information space where documents and other web resources can be accessed through the Internet using a web browser.
WWW is another technical term that is closely related to the Internet. While most common folk will mistake the Internet and WWW to be the “same thing”, take note of the definition here.
The WWW is an “information space” on the Internet. Yes, they are not the “same thing”. The Internet refers to the actual infrastructure, while WWW is referring to the content on the Internet.
A SHORT HISTORY OF THE INTERNET
EARLY IDEAS (1900s)

Once upon a time in the 1900s, the idea of a worldwide information network already existed. Nikola Tesla, the famous superbrain guy actually built an experimental wireless transmission station known as the Wardenclyffe Tower (or Tesla Tower).
What the tower is supposed to do, is to transmit messages wirelessly across the globe, using the Earth itself. But ahem… This project didn’t quite get enough funding nor worked out properly. The tower is later disassembled to sell as scraps, and it is no longer standing today.
EARLY DEVELOPMENT (1960s)
It was not until the 1960s that the “first version” of the Internet came into existence. It all began when the U.S Department Of Defense funded a project called Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET). The idea is simple – Link a group of computer devices together to create a communications network. Link many of such networks together to create a bigger robust network.
Remember that the Internet is a worldwide collection of computer networks? Yes, this simple idea of “link computers to more computers” eventually grew into the worldwide network known as the Internet today.
COMMERCIALIZATION (1980s)
In the 1980s, British computer scientist Tim Berners-Lee came up with the idea of putting up hypertext documents on the network. This may sound like some kind of rocket science, but a “hypertext document” is essentially just… text with links to other documents. Yes, this is known as “website” and “web page” today.
In any case, this idea intrigued and sparked a lot of commercial interest. The Internet boom followed, and by the mid-1990s, the Internet is already a well-known existence. Forever changing the way people communicate, do business, and share information.
MODERN INTERNET (NOW)
As computer technology became better, the Internet also evolved from being “text-only” to all kinds of funky stuff:
- Blogs
- Vlogs
- Podcasts
- Social Media
- eCommerce
- Internet Telephone
- Video Calls
- Video Sharing
- Messaging
- 360° Videos
- Gaming
- Virtual Reality
- Augmented Reality
Even to this day, the Internet is still evolving with more exciting stuff coming up.
BASIC TECHNICAL STUFF

So far so good? Now that we are done with the history, how does one connect to the Internet? Here are some of the basic networking and technical stuff, in layman’s terms.
CONNECTING TO THE INTERNET
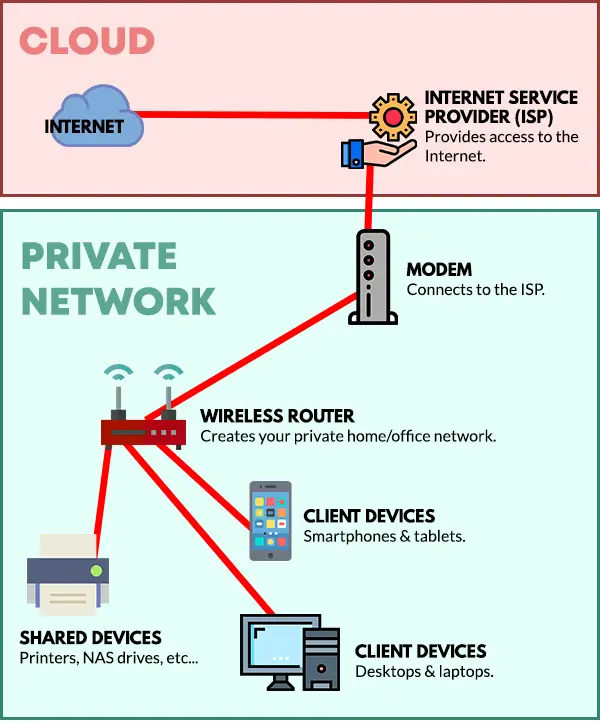
As you already know, we don’t just randomly find a magic connector in the wall and get connected to the Internet.
- Modem – First, we have to subscribe to an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The ISP will provide a device called a “modem” (modulator-demodulator). This is the one that connects to the Internet.
- Wireless Router – Yes, we can directly plug a computer into the modem. But to share the Internet connection, we will use a wireless router to create a private home/office network first.
- Devices – Lastly, simply connect all the devices to the WIFI network. Computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and even other devices such as network printers.
WIRELESS MOBILE NETWORK (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, 6G)
2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, or 6G. This is something that you will hear quite often and it is commonly confused with WIFI. Well, there is nothing much to be puzzled with. There are 2 general ways to connect to the Internet:
- As above, sign up with an ISP. They will provide a modem to connect to the Internet.
- Secondly, sign up for a mobile plan with the ISP. They will provide you with a phone number and an Internet connection through the mobile network. That is, the smartphone will act as a wireless modem.
So yes, WIFI and “G” are two different technologies.
- The “G” stands for “X generation mobile network”. Second-generation mobile network, fifth-generation mobile network, etc…
- Mobile networks usually cover entire cities, they are public networks.
- WIFI networks are created using a wireless router. They are private networks that is within our own home/offices only.
BASIC TECHNICAL TERMS

Websites are probably one of the main “things” that you will find on the Internet. But apart from that, there are also a number of technical terms. These are actually pretty simple terms, but geeky technical folks somehow love to make them sound difficult.
- Website – A site on the Internet that serves information or provides a service.
- Webpage – A page on the website.
- Web Browser – What you are using right now. An application that is used to “surf the Internet” and to visit websites.
- URL – Uniform resource locator, or simply the web address.
- HTTP and HTTPS – HyperText Transfer Protocol (the additional “s” stands for “secure”). Basically, a set of rules that define how data should be sent across the Internet.
- Host – Very simply, a server.
- Client – Any device that is connected to a server.
- HTML – Hypertext Markup Language. The raw coding behind how websites are being formatted.
- Upload – When you transfer data from your own computer device to another.
- Download – When you transfer data from another computing device to your own.
COMMON INTERNET SERVICES

For this final section, let us walk through some of the common Internet services.
SOCIAL MEDIA NETWORKS
Social media networks are the phenomenon that hit the world sometime in the 2000s. These are simply websites that allow you to connect with friends, send messages, share some photos, and even short video clips of your everyday life. A couple of the popular ones are:

I guess this one is pretty much self-explanatory. Email is practically the short form for electronic mail, the digital version of postal mail. There are plenty of free reliable ones you can sign up for on the Internet:
CLOUD COMPUTING
“Cloud” is another term that you will stumble upon. In simple terms, “cloud computing” refers to using digital resources on the Internet instead of your own computer. For example:
- Cloud Drive – Save files on a server somewhere on the Internet.
- Cloud Accounting – Instead of buying and installing accounting software, the financial data and reports are directly done on through the Internet instead.
- Gaming-On-Demand – Instead of having to buy a physical gaming console and a physical copy of the game – Play right through the Internet on any device.
- Cloud Collaboration – Share documents on the Internet, and let your own team (or the public) co-author the project.
Of course, there are many more cloud services, and the number is still growing. Cloud computing is interesting in the sense that it can be accessed anywhere as long as you have an Internet connection – With any supported device. But of course, the disadvantage is that you will need an Internet connection to access the cloud services.
SECURITY
Finally, the Internet is not the safest place… Apart from computer viruses, there are all kinds of malware, trojan, worms, and even phishing – Fake websites that look like actual ones to fool people into entering their email and password. I will leave a link to a Cisco article below if you are interested to read about these threats.
USEFUL BITS & LINKS

That’s all for this tutorial, and here is a small section on some extras and links that may be useful to you.
LINKS & REFERENCES
- History of the Internet – Wikipedia
- Internet Basics – GCFGlobal
- Internet Terms – Computer Hope
- Difference between computer virus – Cisco
THE END

Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope this has helped you to better understand, but we have really just scratched the surface. The Internet is still evolving, and things are forever changing – Please don’t stop here and continue learning!
But for now, if you have anything to share with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and may the cyber force be with you.
