Welcome to a beginner’s guide on the basic things to know about computers, and congratulations on taking the first steps into the cyber world. Aye, while most modern computers are pretty much fuss-free these days, the cyber jungle is still deep with many different technologies and changes over the years.
Where do we begin? What are the essential basic computer skills and knowledge? This guide will walk you through a few of the basic stuff, so you don’t get lost in the cyber jungle. Read on to find out!
1) BASIC COMPUTER PARTS
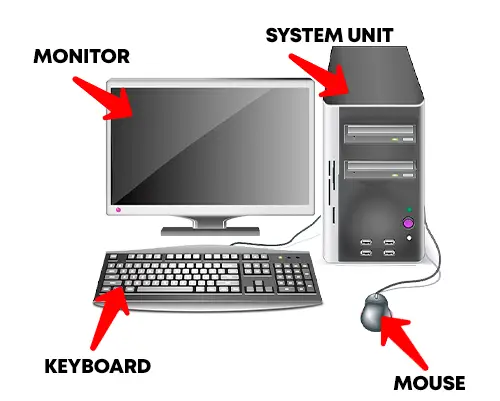
The very first thing you need to know about computers is the parts and what they do. There are probably hundreds of different devices and hardware components, but here are a few of the raw basics:
- Monitor: What you are looking at right now.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT): Once upon a time, computer monitors are big, bulky, and can be used as training weights. CRT monitors are obsolete and rarely used now.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): The technology that took over CRT. LCD displays are thin and use a lot less energy… Not surprising why these got popular.
- Light-Emitting Diode (LED): The common Joe modern-day screen technology that is everywhere – Desktops, laptops, tablets, mobile phones.
- System Unit: Houses the hearts and brains of the computer. Laptops, tablets, smartphones, and all-in-one computers don’t have this “separate unit”, as it is all integrated into one device.
- Keyboard: Don’t think this needs an introduction. What you just used to type characters and numbers with.
- Mouse: Used to move the cursor on the screen, and interact with various elements. You can kind of call it your “digital fingers”.
2) BASIC COMPUTER HARDWARE
Moving on to the internal computer hardware, here are a few of the essentials:
- Motherboard: The heart and “main circuit board” of the computer, to which all the components are connected to.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The mind of the computer, does all the calculations and data crunching.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): For temporary storage of data, used by the CPU for quick calculations and processing.
- Data Storage (Hard Disks and Memory Cards): Where all your data is permanently stored.
- Graphics Card: Also does processing like a CPU. But it specializes in graphics, images, and videos.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The cousin of the CPU, the “main processor chip” on the graphics card.
That’s all for the basic computer parts. But of course, there are a lot more computer parts and devices, follow up with my other guide on the basic computer parts if you want.
3) BITS & BYTES
When it comes to memory and storage space in computers, we quantify it in bits and bytes.
- Computers can only understand 1 or 0, we call this the “binary number system”.
- A single “1 or 0” is called a “bit”.
- 8 bits make up 1 byte.
- 1000 bytes make up 1 kilobyte, 1000 kilobytes make up 1 megabyte, 1000 megabytes make up 1 gigabyte, 1000 gigabytes make up 1 terabyte, and 1000 terabytes make up 1 petabyte.
Yep, that is an insane number of “ones and zeros” that computers are dealing with these days.
4) OPERATING SYSTEMS
What the heck is an operating system? Simply put, a computer is just a collection of hardware components, devices, and an “empty shell”. The operating system is a piece of software that acts as a platform which you install applications upon – It handles all the coordination between the hardware, so you don’t have to worry about it. A few popular operating systems are:
5) SHORTCUT KEYS
Stop fumbling through the menus, shortcut keys can help you to navigate a lot faster. Here are a few common ones that you have to know.
| Windows-E | Open “My Computer”. |
| Windows-Up Arrow | Maximize the current window. |
| Windows-Down Arrow | Minimize the current window. |
| Windows-Left Arrow | Move the current window to the left. |
| Windows-Right Arrow | Move the current window to the right. |
| Windows-D | Minimize all windows. |
| Alt-F4 | Closes current window. |
| Windows-L | Lock your computer. |
| Alt-Tab | Switch between windows. |
| Command-N | Open a new finder window. |
| Command-M | Minimize the current window. |
| Command-W | Close the current window. |
| Command+` | Switch between windows. |
| Command+Shift+Q | Log out. |
| Ctrl-C or Command-C | Copy |
| Ctrl-X or Command-X | Cut |
| Ctrl-V or Command-V | Paste |
| Ctrl-Z or Command-Z | Undo |
| Ctrl-Y or Command-Y | Redo |
6) BASIC SYSTEM CONTROLS
When it comes to system settings, beginners tend to freak out instantly. Yes, things can go wrong if you mess with the wrong things, but you still need to learn how to control your own system. How about starting with how to manage/uninstall the apps that you don’t use?
WINDOWS
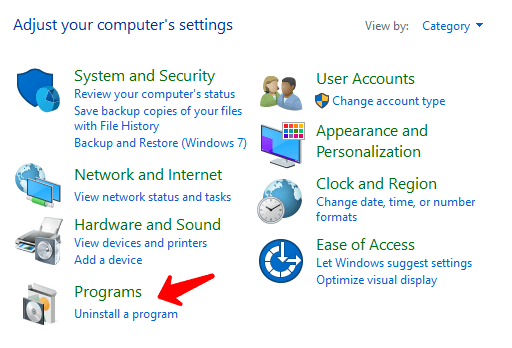
Start button > Search for control panel > Under programs, uninstall a program. Feel free to explore the rest of the control panel, and maybe change the wallpaper under appearance.
MAC OSX
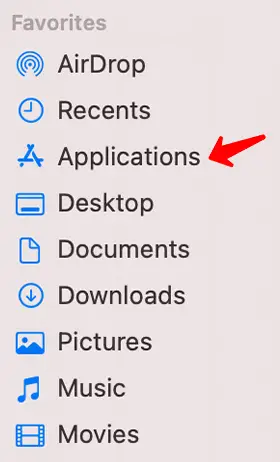
Uninstalling applications on a Mac is slightly different – Open a finder window > Applications > Drag and move an application into the trash bin. To access the “control panel”, click on the Apple icon on the top left side of the screen > System Preferences.
7) BASIC TROUBLESHOOTING
So what do we do when computers act strange or stop responding? There is this simple golden rule of troubleshooting ever since the ancient days –
- Try to stop the application that is causing trouble.
- Force shut down and restart the computer if it is totally unresponsive.
WINDOWS
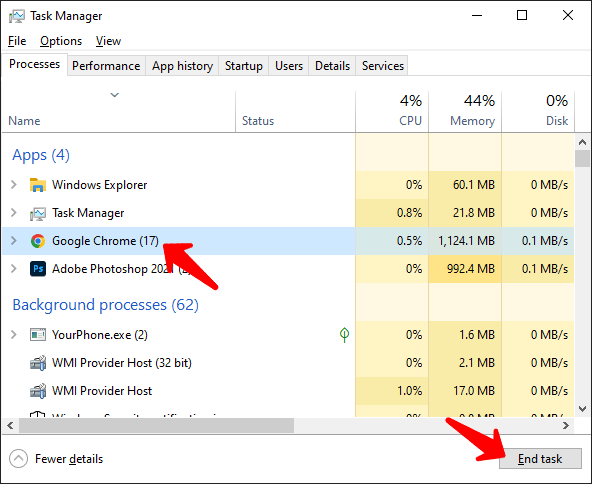
If your Windows PC becomes unresponsive, try pressing control-shift-escape to launch the task manager. Applications that are causing trouble will usually be highlighted as “not responding”, or they usually eat up 100% CPU. Select that application, and hit “end task”.
MAC
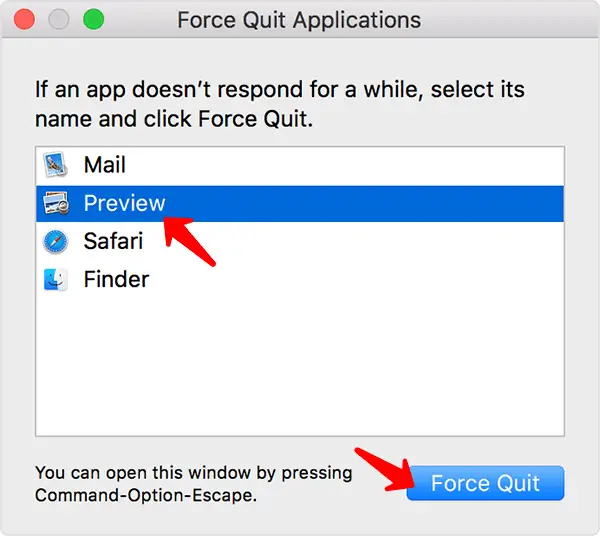
Similarly, on a Mac, press command-option-escape to open up the force quit window. Applications that have gone to the moon will be highlighted as “not responding”. Select the problematic application, then hit “force quit”.
IF ALL ELSE FAILS
If force closing the application did not work, press and hold the power button on your computer for at least 4 seconds. That will immediately power off the computer.
As you switch on the PC again, it may complain something about “not shutting down properly”. If everything returns to normal afterward, then that is good. But if it is still acting strange, you will need to get some professional help.
8) BASIC MAINTENANCE
Computers are pretty much fuss-free these days, but they are not exactly maintenance-free. It is still good to do some routine maintenance on both the software and hardware once in a while:
- Clean the dust off the fans, allow good ventilation, and for the sake of your own health as well.
- Clean the gunk off the keyboard and mouse… They are magnets for dust, dirt, food bits, and even your own skin/broken fingernails.
- Free up some space, and uninstall apps that you don’t use anymore.
- Update the OS, anti-virus, and apps.
Follow up with my other guide on how to maintain your computer if you want.
9) BASIC NETWORKING
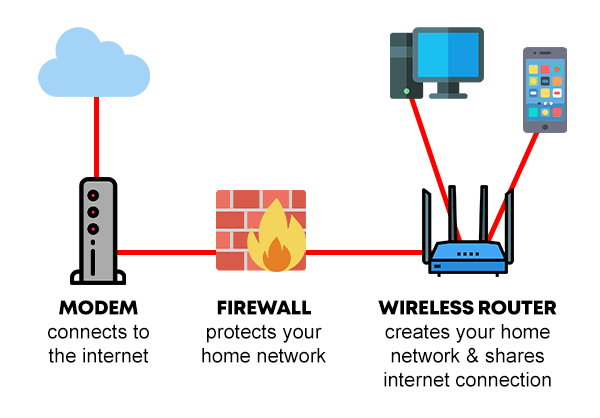
Yes, there is no need to become a networking wizard, but it is good to know some of the basics. At least understand some of the networking devices and what they do.
- Modem: Short for modulator-demodulator, this device connects you to the Internet.
- Firewall: A device that protects your private (home) network, always good to have but not mandatory.
- Wireless Router: This is the one that creates your private network, where you connect your devices to share the Internet connection.
- Repeater/Wireless Booster: If you live in a large house, there will be “dead corners” where the range of the wireless router cannot reach. A repeater or booster is as the name implies, it is used to boost the range of the wireless router.
10) INTERNET BASICS
While we are still on the topic of networking, here is a short section on the confusing Internet stuff.
- What is the Internet? – The Internet began as an idea for military use. By connecting many computers and networks together, they can relay messages and communicate with each other. This idea eventually “grew out of control” on a global scale, and it became the “Internet” today.
- IP – Stands for Internet Protocol, which is basically a set of rules on how computers communicate with each other.
- IP Addresses – We give a unique IP address to each device in a computer network to identify them, much like giving them a street address… So that we can deliver the correct data packets to the correct computer.
- DNS – Who the heck remembers places by their exact street address? This is why we give location names such as XYZ shopping mall and ABC park. It works the same way on the Internet, and who will remember websites by their IP addresses? This is why we have the Domain Name System (DNS) which will map a given website address to the IP address.
- URL – Stands for Uniform Resource Locator, which is just a “hardcore technical” way of saying “website address”.
11) WIRELESS FILE SHARING
One way to share files between 2 computers is to use a USB Flashdrive. But when you are connected to your own home network, there are more convenient ways to do, and you can try out free apps such as Send Anywhere and Share It. Alternatively, you can also use cloud drives such as Google Drive, One Drive, and Dropbox.
12) REMOTE CONTROL YOUR COMPUTER
Don’t we all have those times when we left some important documents or forgotten to copy work out from the computer? Thankfully with the help of technology, you can actually remote control your computer through the Internet… Provided that you left the computer on, and connected to the Internet. You can check out:
This is also pretty useful if you have smart home devices attached to your computer, enabling you to remote control your own house.
- Monitor your security cameras through the computer.
- Lock and unlock doors.
- Switch on the air conditioner before you reach home.
- Switch on/off the lights, and open/close the windows.
13) SECURITY
Finally, the world is full of shady stuff these days, and it is best to get some protection. While having anti-virus software installed on your computer does not make it totally immune to virus and cyber attacks, it does still offer a layer of protection.
While a locked door can still be broken down, it does take quite a lot of effort to do so, and it does keep a lot of those wannabe robbers away. You can check out some of these free anti-virus software.
THE END

Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this guide. I hope this has helped you to better understand, and if you have anything to share with this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and may the cyber force be with you.


This is very helpful….
thanks so much
Hey…I just want to take this chance and thanks you guys for the above guidelines, which I got to say they are well framed such that they are clearly giving someone a guideline incase of a personal extensive Study which I just embarked on…can’t wait to explore more with you..,Cheers!
It was interesting reading this page
nice guysshah
Thank You it was interesting and informative to read your article.